

- Wake magic packet sender how to#
- Wake magic packet sender install#
- Wake magic packet sender software#
- Wake magic packet sender Pc#
338929 files and directories currently installed.) Selecting previously unselected package etherwake. Get:2 focal/main amd64 wakeonlan all 0.41-12 Get:1 focal/universe amd64 etherwake amd64 1.09-4build1 The following NEW packages will be installed:Ġ upgraded, 2 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.Īfter this operation, 56.3 kB of additional disk space will be used. The following additional packages will be installed:
Wake magic packet sender install#
Type the following apt-get command/ apt command to install the same under Debian / Ubuntu Linux desktop:Į: Unable to locate package backups]$ sudo apt install etherwake We use the etherwake command to send a Wake-On-LAN “Magic Packet” under Linux operating systems. Linux Install etherwake Under Debian / Ubuntu Linux You will find various tools for all modern operating systems, including MS-Windows 8/10, Apple macOS & OS X, all modern Linux distros, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD and many smartphones.
Wake magic packet sender software#
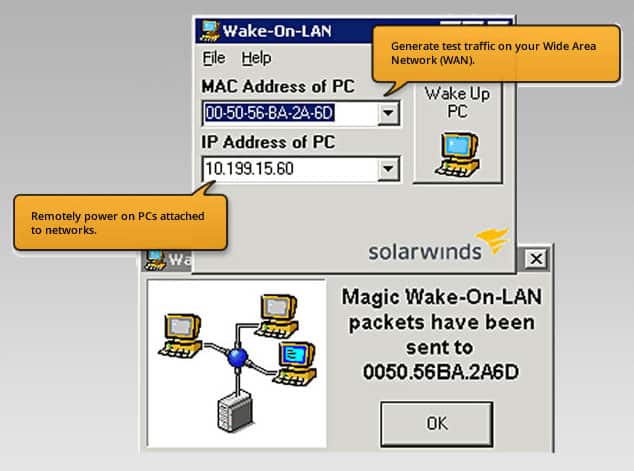
n.2.It would be best if you used software to send WoL ( Wake-on-LAN ) magic packets to the target system.
Wake magic packet sender Pc#
Generate the magic packet from the server and the PC should wake up. Note: In this example with 'wakeonlan', the MAC address required to build the magic packet has to be reversed compared to the PC real MAC address (00:11:d8:12:89:17)įor more information, please look at the linux man page Linux wakeonlan command line used in this example:

#3 : Static ARP entry to force destination MAC for the magic packet to be a broadcast #2 : Policy to allow general traffic to the PC #1 : Policy to allow the Wake On Lan "magic packet" using its dedicated IP Note : using the PC IP (instead of another IP) in the static ARP entry would work to wake the PC up, but this may break other traffic destined to the PC. Forwarding the packet as a broadcast is achieved with a static ARP entry with mac FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF. For this, we use a different IP address for the magic packet to reach the PC than the main PC IP address (choose an IP address not used on the PC subnet). The main problem is to get the magic packet forwarded as a broadcast once routed to get it recognized by the PC NIC. Packet is received from "PC to wake up" network interface and triggers the Wake on Lan startup.
The WOL packet is received from the FortiGate DMZ and routed to "PC to wakeup" as an Ethernet broadcast. "Server" sends a Wake On Lan Magic Packet to "PC to wake up". This is the particular case which is discussed here. In some cases, a unicast destination IP can be used which makes the routing straight forward, however most generally the destination MAC of the magic packet must be a broadcast which causes a routing problem. There are different types of Magic Packets that can be used depending on the NIC manufacturer and driver. This requires the PC network interface and BIOS to support WOL. The idea of Wake On Lan (WOL) is to trigger the "wake up" (boot-up) of a device from the LAN via a specific Ethernet packet called 'Magic Packet'. This example is based on broadcast type of Wake On Lan "magic packet".

Wake magic packet sender how to#
This document provides an example of how to configure the FortiGate to route "Wake On Lan magic packet".


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
